Introduction: Why is B2B Payments Modernization Essential for US Businesses?
Imagine if you had no access to technology in your workplace for one day.
No phone, no internet, nothing.
Sounds really tough, right?
In the fast-paced world of business, technology is paramount. However, the same analogy applies to landscape of B2B payments in the US. Despite vast technological advancements in finance, it has remained burdened by manual processes.

Source: FedPayments Improvement
2023 is the year for change, and that change is coming in the form of B2B payments modernization. It digitizes the whole Order-to-Cash cycle enabling straight through processing (STP) which involves electronic transfers and eliminates the need of manual intervention.
The two core parts of straight through processing are: e-Invoicing and e-Remittance. E-Invoicing is the exchange of an invoice between a supplier and a buyer in an integrated electronic format and e-Remittance is the electronic communication sent from a customer to a business to convey payment or financial transaction details.
In this blog, we will dive deep into how e-Remittance exchange framework can help your business in payments modernization. Let’s start with understanding the need for shifting away from manual remittance processing.
The Reality of Manual Remittance Processing and e-Remittance
Do you remember those days when remittances were sent by couriers and your finance team had to manually check and enter them into the accounting systems? It was indeed a resource-intensive process.
Well, it’s easy to get stuck doing what you’ve always done. Hence, most businesses often overlook the real cost behind it and continue to do manual remittance processing. Here are some of the main benefits of e-Remittance over manual remittance processing:
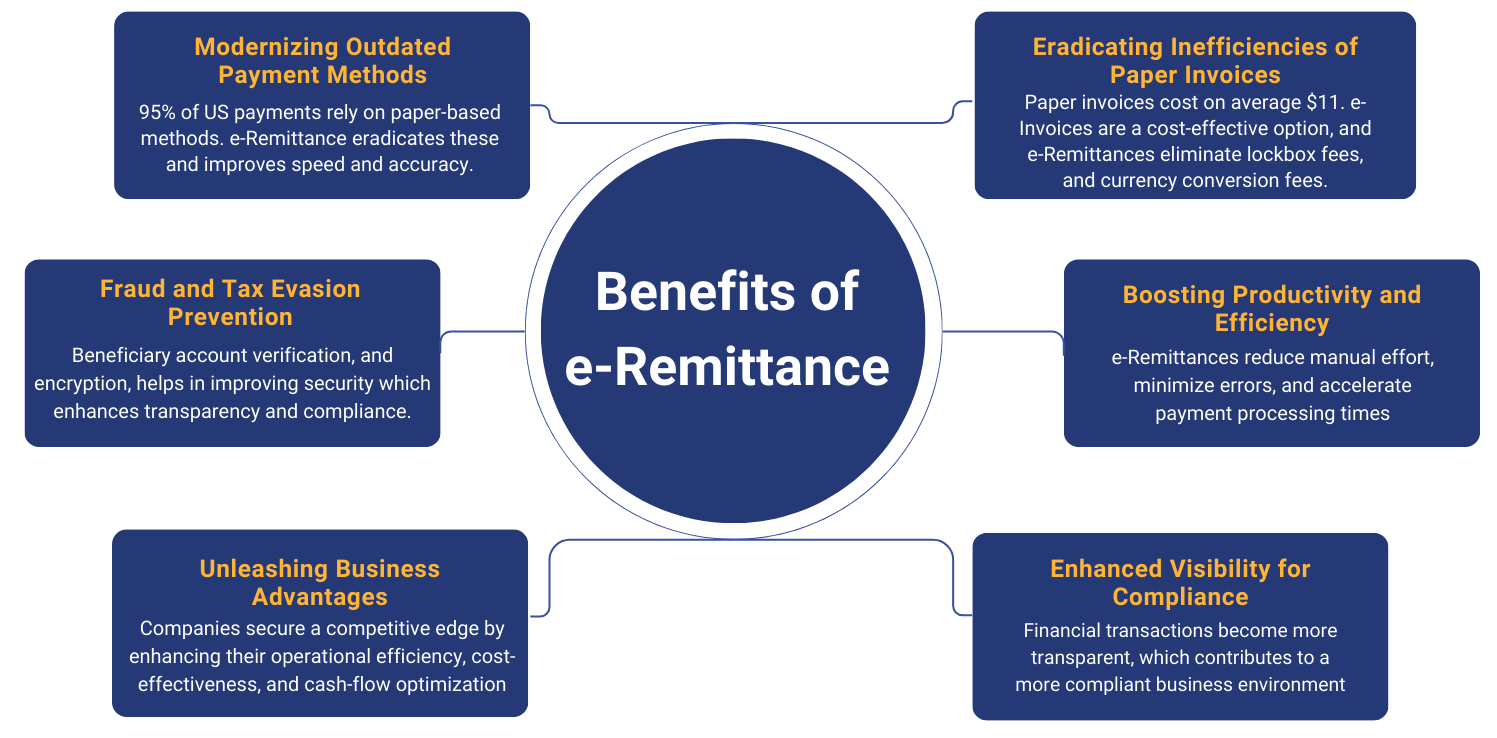
Now you can understand the real value of e-Remittance, but setting up an e-Remittance ecosystem in the US comes with its own set of challenges. Next, let’s take a closer look at the barriers of e-Remittance delivery and processing.
Identifying the Barriers Of e-Remittance Delivery and Processing
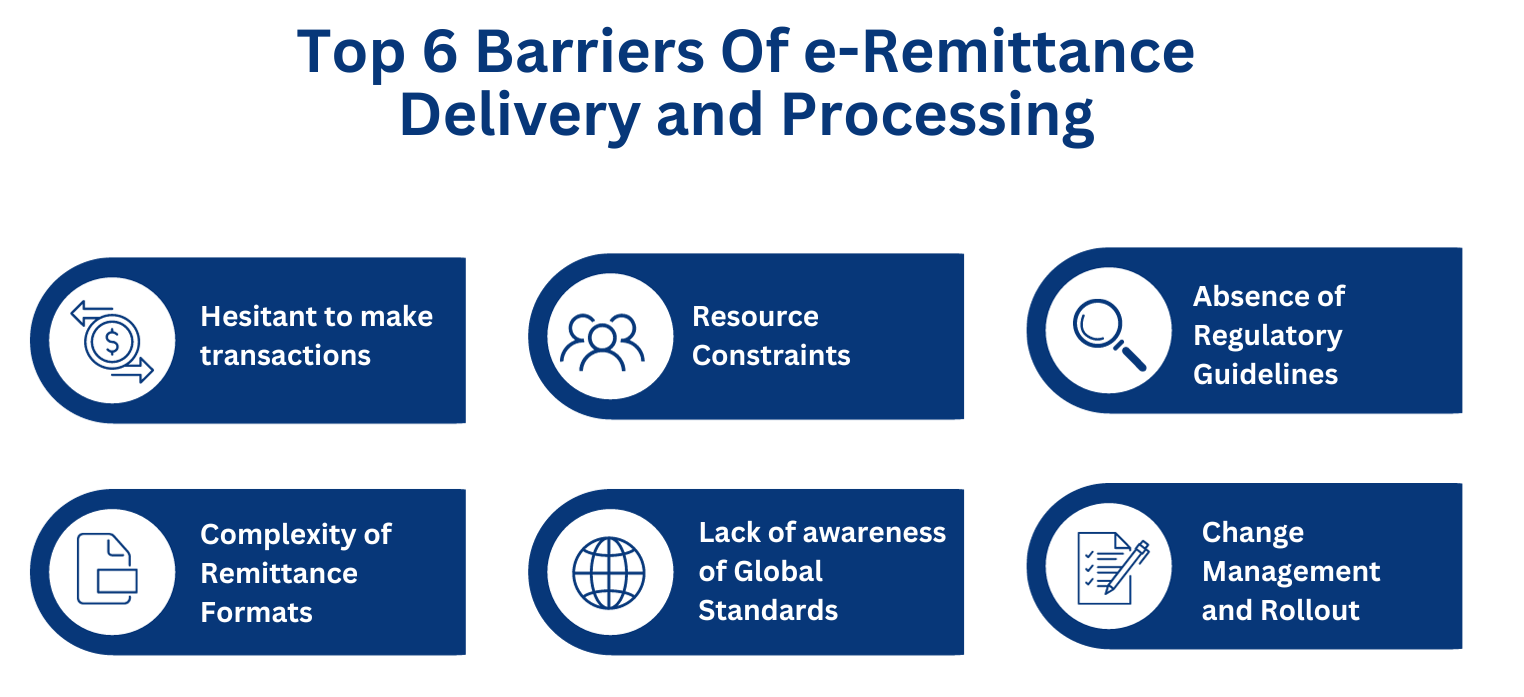
There are several barriers to the delivery and automated processing of e-Remittance. Here is a list of the key ones:
1. Hesitant to make transition from paper checks:
Despite the decline in B2B check payments to an all-time low of 33% in North America, a significant portion of mid-market US businesses still prefer paper checks for their disbursements. This reluctance is driven by challenges in convincing both customers and suppliers to embrace electronic payment methods.
2. Lack of Awareness of ISO 20022 and Interoperability Issues:
Many businesses are unfamiliar with ISO 20022, the global standard for new payment systems. This hampers the adoption of standardized formats for payment files. The absence of common standards and interoperability in electronic payment systems presents challenges to share a common understanding and language in electronic payment processes.
3. Complexity of Remittance Advice Bank Formats:
In the US, there are over 4000 commercial banks, businesses dealing with numerous buyers who maintain accounts across various banks face difficulties in reconciling payments with remittance information. Also, different payment types support different formats of remittances which is further complicated by sector specific requirements such as Healthcare remittance data is very different from a remittance in the automanufacturing sector. This complexity hampers the global adoption of electronic payments, even in regions with higher electronic payment penetration.
4. Resource Constraints for Mid-Size Businesses:
Mid-size businesses encounter barriers related to costs, IT infrastructure, and training due to limited budgets. Integration issues further compound the problem, as mid-size businesses struggle to integrate electronic payments with their existing ERP systems and back-office platforms.
5. Absence of Regulatory Guidelines:
In numerous countries, governments have enforced mandatory requirements for businesses to transition to digital frameworks such as the e-Invoicing mandate. Countries where such initiatives are not present have seen a lower rate of adoption for electronic exchange of invoices and remittances.
6. Change Management and Rollout:
The intricacies of change management and rollout, especially for mid-sized businesses with limited resources, impedes the smooth adoption of B2B modernization.
What is e-Remittance Exchange Framework?
While analyzing the barriers faced by businesses when trying to connect with each other during e-Remittance delivery and processing, the Federal Reserve and Business Payments Coalition (BPC) gave rise to an e-Remittance exchange framework overseen by Digital Business Networks Alliance.
The BPC and Federal Reserve have been collaborating with industry experts to modernize the exchange of e-Invoicing and e-Remittance data in the US. In September 2021, the e-invoice Exchange Market Pilot was launched. The pilot phase has concluded for e-Invoicing, and the network is now ready to begin the production phase.
Now, they are launching the e-Remittance Exchange Pilot phase to test a virtual network. The mission is to operate an electronic delivery exchange network of remittances, available for use by all businesses in the US. It allows businesses to connect, and share electronic remittances, regardless of the platform, system, or network they use.
It will begin in September 2023 using the Digital Business Network Alliance’s exchange framework. Various businesses in the US are participating and there are three different roles for Pilot participants:
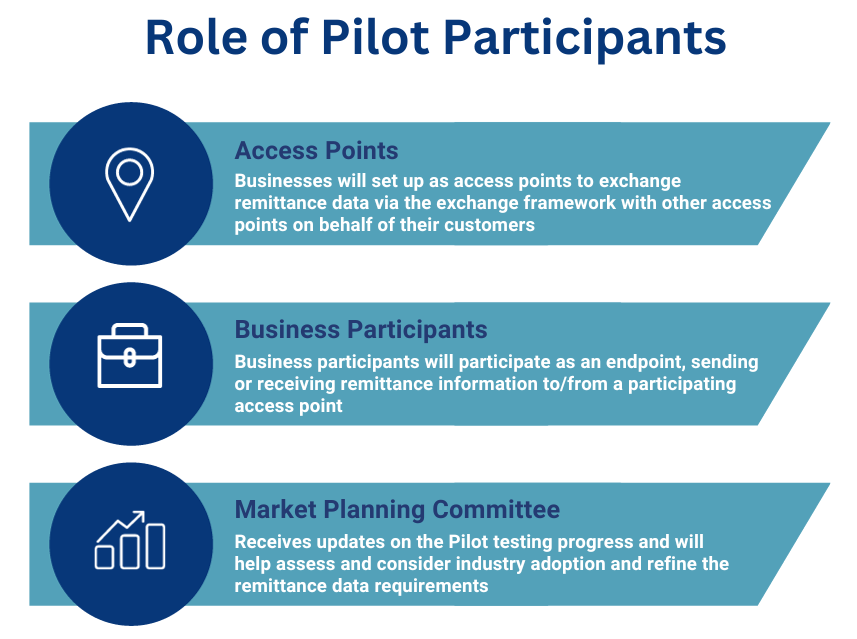
Next, let’s dive deep into the workflow of this e-Remittance exchange network.
How Does the e-Remittance Exchange Framework Work?
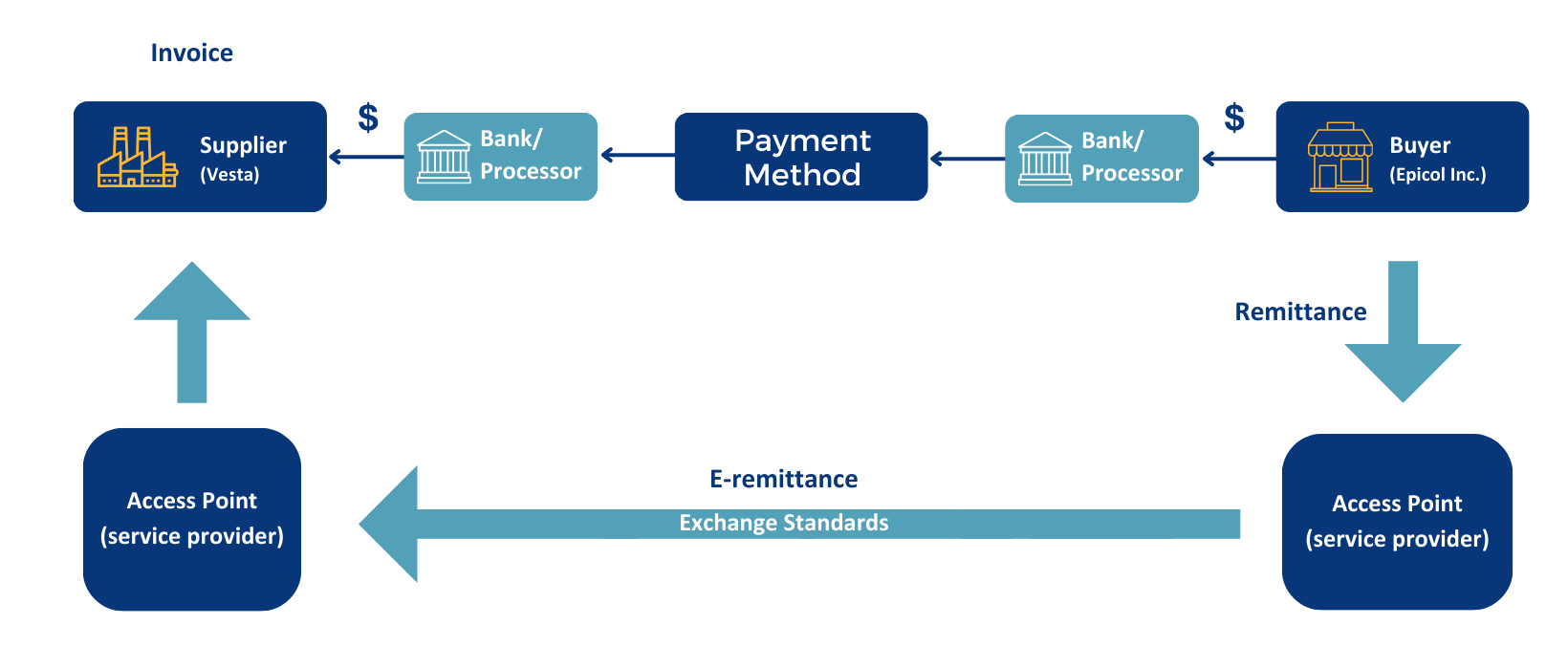
Source: FedPayments Improvement
Imagine a scenario where a buyer, Company Epicol Inc, has purchased 270 pieces of machinery from their supplier, Company Vesta.
We will follow the exchange of e-Remittance using the above framework from Epicol Inc. to Vesta.
Step 1: First, Epicol Inc. generates the remittance advice for the invoices that are paid and sends it to their e-Remittance service provider, also known as access point.
Step 2: Here, Epicol’s access point will deliver the remittance to Vesta’s access point.
Step 3: Next, Vesta’s access point converts the remittance advice into the required format for Vesta’s AR system and sends it electronically to them.
Step 4: Vesta’s AR system then automatically reconciles the payment, extracting the necessary data, and posts it directly to their ERP system.
This e-Remittance exchange framework supports all payment methods and requires minimal to no change to existing systems.
Now, we have gained a clear understanding of the workflow of e-Remittance exchange framework. But to build this e-Remittance ecosystem, there are certain entities which should operate collaboratively to provide a frictionless payment processing experience.
Building the Ecosystem Of e-Remittance Exchange Framework
This standardized ecosystem of e-Remittance aims to facilitate straight-through payment processing. It’s a pivotal step toward a more unified B2B payment space and requires a collaborative effort and partnerships to make this a success.
- Banks and Fintech Partnerships
Banks and Fintech have recognized the strategic importance of offering integrated financial services to corporate clients, leading to increased demand for value-added solutions. These partnerships open new revenue streams for services like EIPP and reconciliation.
- ERP capabilities and Partnerships
Fintechs need to partner with top ERP software providers that serve both the mid-market and enterprise markets in US such as Acumatica, Sage Intacct, Oracle NetSuite, also with large ERP providers like SAP, Oracle, IFS. These partnerships are essential for creating an interconnected financial ecosystem.
- Industry Groups Collaboration
Collaboration with industry verticals like CPG, Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Retail, Pharma showcases the versatility in addressing the specific needs of diverse sectors and the ability to operate despite unique industry challenges.
- Payment and Fintech Groups Collaboration
Partnerships with payment groups such as FCC (Fintech Convergence Council) underline the dedication to staying at the forefront of payment technologies and regulatory advancements, ensuring that solutions are in par with industry standards and compliance requirements.
- Financial Advisory, and Consulting Organizations Partnerships
Engaging with renowned accounting & consulting firms such as Deloitte, KPMG, and more, showcases the commitment to forging impactful partnerships within the accounting and financial transformation consulting industry.
Another important aspect of this exchange framework is open-source technologies. It comprises of open-source tools such as Apache NiFi, Kubernetes, etc. and registry services such as Zookeeper. Platforms built upon a foundation of these open-source technologies empower seamless interactions between buyers, sellers, and financial institutions. It ensures that payment data from various sources are efficiently processed and shared between parties, reducing manual effort and errors.
Major Initiatives for Smooth Adoption of the Exchange Framework
There are certain initiatives taken by Fintechs which will help businesses to adopt the e-Remittance exchange framework successfully once it launches in market. Here are a few major initiatives:

In the next section, let’s check out some other geographies and discover the exchange framework.
Exchange Frameworks Across the Globe
Numerous countries around the globe have already implemented electronic exchange networks, and many others are actively working towards the implementation. Here we will focus on the major exchange frameworks of these geographies:

- Europe:
Pan European Public Procurement Online (PEPPOL) is a series of initiatives to promote payment modernization in B2B and B2G sectors. It enables companies to send and receive electronic invoices, waybills, etc., regardless of what country they are in. It was originally only available in European countries but rapidly expanded out of Europe. Currently, it is operating in 38 countries.
- India:
On October 1, 2020, the government introduced the e-invoicing system as a part of its digitalization efforts to standardize the invoicing process. For all entities having turnover above INR 50 million, doing B2B transaction invoices are to be mandatorily registered electronically on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). The portal creates a unique identifier for each invoice and returns an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and a QR code to the entity participant. e-Invoice has benefitted businesses with standardization, inter-operability, auto-population of Invoice details into GST return and other forms (like e-way bill), reduction in processing costs, reduction in disputes, improvement in payment cycles and thereby improving overall business efficiency. GSTN’s mission is to help taxpayers with a seamless e-Invoice compliance by laying down standards for invoicing, and GST reporting mechanism so as to receive timely input credits.
- France:
France started introducing mandatory e-Invoicing for suppliers to government entities in 2017. The French government chose Chorus Pro as the official platform for businesses to issue e-invoices to public administrations. From January 2020, all suppliers to the public sector (B2G) have been required to issue invoices electronically. B2B e-invoicing will become mandatory for large businesses in 2024, with medium and small businesses following in 2025 and 2026 respectively.
- Italy:
Italy has introduced mandatory real-time electronic sales invoice issuance and reporting from 1 January 2019. All relevant invoices must be issued and submitted to the Italian Revenue Agency’s e-invoicing platform, Sistema di Interscambio (SdI).
- Hungary:
In 2018, Hungary established a legal framework: Real Time Invoice Reporting (RTIR), requiring businesses to use a designed schema to report invoice data to the tax authority in real-time for domestic transactions.
Next, let’s find out how Fintech companies can help in optimizing remittance processing.
How Fintechs Can Help Businesses Adopt the e-Remittance Exchange Framework?
With the rise of e-Remittance exchange framework it is forecasted that e-Remittance and e-Invoicing will become mandatory for B2B businesses within the next few years in the US. But how will mid-sized businesses adopt this?
Fintechs provide automated solutions that digitize remittance processing, enhancing efficiency, affordability, and accessibility. These solutions provide B2B businesses with a platform where they can send/receive e-Remittances and can seamlessly adopt the exchange framework.
The journey toward B2B payment modernization with e-Remittance exchange framework is transforming the landscape of financial operations. Global PayEX stands as a partner in this journey, offering AR/AP automation solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing ERP, and optimizes the Invoice-to-Cash cycle with the power of AI to achieve 95%+ STP. Talk to our experts to know more.